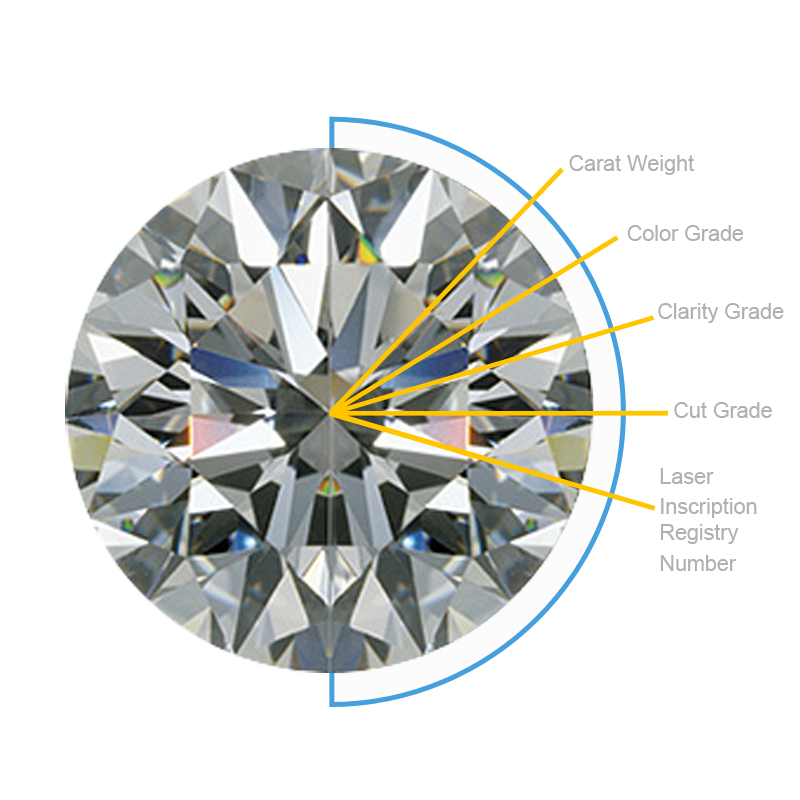
DIAMOND KNOWLEDGE
This is guide for knowlage base about diamond for your information
COLOUR

Diamonds come in a variety of colors, some of them highly prized (pink, blue, even yellow). However in a white diamond, the presence of a yellow tint will lower the price of a diamond. The less body color in a white diamond, the more true color it will reflect, and thus the greater its value.
GIA’s D-to-Z color-grading scale is the industry’s most widely accepted grading system. The scale begins with the letter D, representing colorless, and continues, with increasing presence of color, to the letter Z.
Many of these color distinctions are so subtle that they are invisible to the untrained eye; however, these distinctions make a very big difference in diamond quality and price.
CLARITY
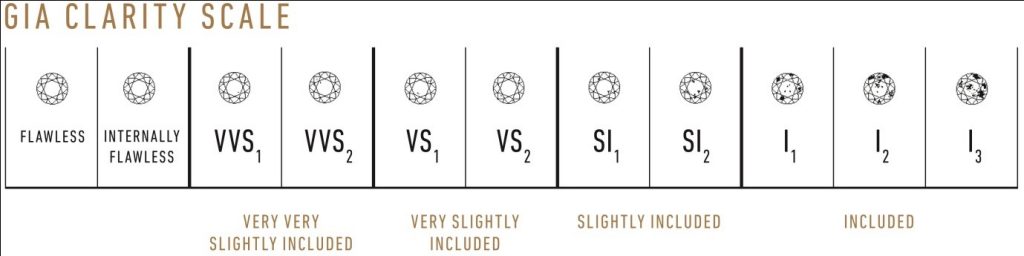
Evaluating diamond clarity involves determining the number, size, relief, nature, and position of these characteristics, as well as how these affect the overall appearance of the stone. While no diamond is perfectly pure, the closer it comes, the higher its value.
Many inclusions and blemishes are too tiny to be seen by anyone other than a trained diamond grader. To the naked eye, a VS1 and an SI2 diamond may look exactly the same, but these diamonds are quite different in terms of overall quality. This is why expert and accurate assessment of clarity is extremely important.
CUT
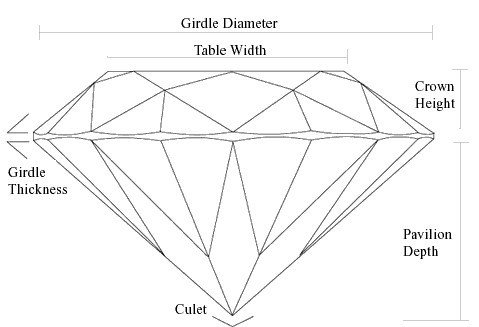
Diamond cut is the summary of a diamond’s proportions evaluated using the attributes of brilliance, fire, and scintillation. While high grades of color or clarity affect a diamond, it’s the cut that determines its overall proportions and its ability to reflect light.
CARAT

Diamonds are weighed in diamond carat weights. A carat weighs 200 milligrams. Diamond professionals also use the point system for smaller diamonds, with 100 points being equal to one carat. A carat is usually abbreviated to ct.
Ct. refers to total carat weight. It is the total weight of all the diamonds in a piece of jewelry.

